在学习了将ffmpeg引入到Android Studio工程中,下面我们来尝试使用ffmpeg使用软解码将一个视频文件解码为yuv文件。
通过解码为YUV数据,我们可以给视频添加一些特定的效果,比如抖音的各种动效等等。
我们通过一张图看一下解码过程,以及需要使用到的ffmpeg的api:
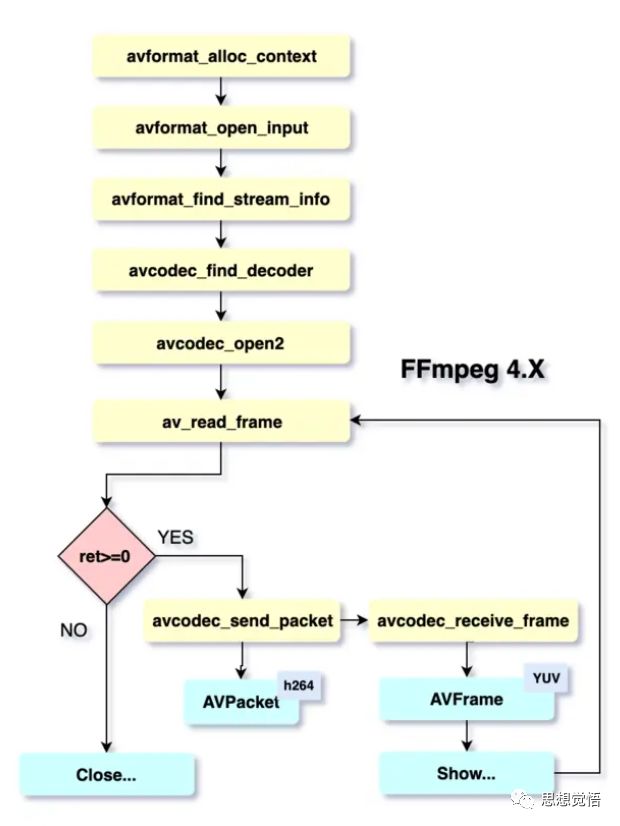
废话少说,直接上菜。
首先编写java的Native方法:
/**
*
* @param videoPath 视频文件路径
* @param YUVoutPath yuv文件输出路径
* @return
*/
public native static int decodeVideo2YUV(String videoPath,String YUVoutPath);编写JNI代码:
// 头文件
// 因为ffmpeg是纯C代码,要在cpp中使用则需要使用 extern "C"
extern "C" {
#include "libavutil/avutil.h"
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
}
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_com_flyer_ffmpeg_FFmpegUtils_decodeVideo2YUV(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jstring video_path,
jstring yuvout_path) {
const char *inPath = env->GetStringUTFChars(video_path, 0);
const char *outPath = env->GetStringUTFChars(yuvout_path, 0);
AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx;
// 初始化格式化上下文
fmt_ctx = avformat_alloc_context();
// 使用ffmpeg打开文件
int re = avformat_open_input(&fmt_ctx, inPath, nullptr, nullptr);
if (re != 0){
LOGE("打开文件失败:%s",av_err2str(re));
return re;
}
//探测流索引
re = avformat_find_stream_info(fmt_ctx, nullptr);
if(re < 0){
LOGE("索引探测失败:%s",av_err2str(re));
return re;
}
//寻找视频流索引
int v_idx = av_find_best_stream(
fmt_ctx, AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO,-1, -1, nullptr, 0);
if (v_idx == -1){
LOGE("获取视频流索引失败");
return -1;
}
//解码器参数
AVCodecParameters *c_par;
//解码器上下文
AVCodecContext *cc_ctx;
//声明一个解码器
const AVCodec *codec;
c_par = fmt_ctx->streams[v_idx]->codecpar;
//通过id查找解码器
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(c_par->codec_id);
if (!codec){
LOGE("查找解码器失败");
return -2;
}
//用参数c_par实例化编解码器上下文,,并打开编解码器
cc_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
// 关联解码器上下文
re = avcodec_parameters_to_context(cc_ctx, c_par);
if (re < 0){
LOGE("解码器上下文关联失败:%s",av_err2str(re));
return re;
}
//打开解码器
re = avcodec_open2(cc_ctx, codec, nullptr);
if(re != 0){
LOGE("打开解码器失败:%s",av_err2str(re));
return re;
}
//数据包
AVPacket *pkt;
//数据帧
AVFrame *frame;
//初始化
pkt = av_packet_alloc();
frame = av_frame_alloc();
FILE *yuvFile =fopen(outPath,"wb+");//黑皇实体sh_768x432.yuv
while (av_read_frame(fmt_ctx, pkt) >= 0) {//持续读帧
// 只解码视频流
if (pkt->stream_index == v_idx) {
//发送数据包到解码器
avcodec_send_packet(cc_ctx, pkt);
//清理
av_packet_unref(pkt);
//这里为什么要使用一个for循环呢?
// 因为avcodec_send_packet和avcodec_receive_frame并不是一对一的关系的
//一个avcodec_send_packet可能会出发多个avcodec_receive_frame
for(;;)
{
// 接受解码的数据
re = avcodec_receive_frame(cc_ctx,frame);
if(re !=0)
{
break;
} else{
// 数据y
fwrite(frame->data[0],1,cc_ctx->width*cc_ctx->height,yuvFile);
// 数据U
fwrite(frame->data[1],1,cc_ctx->width/2*cc_ctx->height/2,yuvFile);
// 数据V
fwrite(frame->data[2],1,cc_ctx->width/2*cc_ctx->height/2,yuvFile);
}
}
}
}
//关闭文件句柄
fclose(yuvFile);
//关闭环境
avcodec_free_context(&cc_ctx);
// 释放资源
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_packet_free(&pkt);
avformat_free_context(fmt_ctx);
LOGE("解码YUV成功");
return 0;
}这里就不多解析了,代码中的注释已经写写的很清楚了,配合解码流程图和代码多看几遍相信大家都能看得懂。
解码成功后我们发现YUV视频比原始视频数据大得多,比如笔试解码一个原始大小为16兆的视频,解码成功后的数据大概是1186兆,这就是为什么音视频需要编码的原因,如果不编码,现有的宽度速度根本就无法支撑,存储也会大大浪费空间。
那么解码成功后的数据如何显示呢?能不能正常播放呢?在后面的实践中我们继续探索。
本文来自作者投稿,版权归原作者所有。如需转载,请注明出处:https://www.nxrte.com/jishu/19844.html